Understanding the ABCDEs of Melanoma
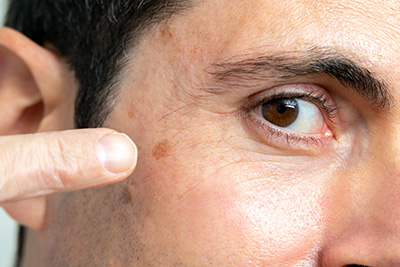
Cosmetic and skin cancer surgeon Dr. Ralph Massey specializes in the diagnosis and surgical treatment of melanoma in Santa Monica, CA. Dr. Massey is a tireless educator and advocate of the vital importance of detecting skin cancer early, especially if melanoma is suspected. Join us for the following insights from Dr. Massey on the ABCDEs of melanoma, a critical tool for helping in the early recognition of this most serious form of skin cancer.
The ABCDEs of Melanoma Explained
Melanoma is a formidable adversary, but knowledge is our greatest weapon in the fight against this condition. The ABCDEs of melanoma represent key characteristics of moles or growths that could signify the presence of cancer. Dr. Massey stresses the importance of familiarizing oneself with these signs:
Asymmetry – One-half of the mole or birthmark does not match the other. Healthy moles are typically symmetrical, so any asymmetry warrants closer examination.
Border – Irregular, scalloped, or poorly defined borders in a mole can be a warning sign. Unlike benign moles that have smoother, more even borders, malignant ones often display uneven edges.
Color – The presence of varied colors within a single growth – including shades of brown, black, pink, red, white, or blue – can indicate melanoma. Uniform coloration is more common in non-cancerous moles.
Diameter – Melanomas usually are larger in diameter than a pencil eraser (6mm). However, they can be smaller when first detected, making it crucial not to overlook smaller suspicious moles.
Evolving: Any change in size, shape, color, elevation, or another trait, or any new symptom such as bleeding, itching, or crusting, points to evolution. A mole that changes over time is a red flag.
Skin Cancer: The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of melanoma can significantly enhance treatment success. Regular self-examinations using the ABCDE guide and annual skin checks by a dermatologist are vital strategies in identifying melanomas at their most treatable stage.
Preventing Skin Cancer: Sunscreen, Lifestyle and Diet can Minimize Risk
The importance of using a proper sunscreen to protect your skin from exposure to Ultra-Violet (U.V.) Light exposure can not be overstated. Whether from the sun or tanning beds, U.V. Light is a known carcinogen that causes the majority of skin cancers. Applying broad-spectrum sunscreen of SPF 30 or higher every two to three hours and wearing protective clothing can significantly minimize the risk for developing melanoma.
While avoiding sun exposure during peak hours and the diligent use protective clothing and sunscreen are the first lines of defense against developing skin cancer, following are some additional preventative measures to consider:
Oral vitamin D supplements – For individuals seeking the therapeutic benefits of the sun or tanning booths, vitamin d supplements have been shown to provide similar benefits in place of sun exposure and the use of tanning beds.therapeutic benefits in place of sun exposure or the use of tanning beds.
Nicotinamide (Vitamin B3) – High-risk individuals can reduce their risk of basal cell and squamous cell skin cancers by over 20% through the twice-daily oral intake of 500 mg nicotinamide (vitamin B3). This readily available supplement is considered safe.
Low Fat Diet – Evidence suggests that maintaining a low-fat diet (less than 20% of calories from fat) over the long term may lower the risk of skin cancer.
Tea Consumption – Incorporating black or green tea into daily consumption habits may slightly reduce the long-term risk of skin cancer.
Skin Resurfacing – Procedures such as CO2 laser or medium-depth chemical peels offer dual benefits: they improve skin appearance while also reducing the risk of further skin cancers in treated areas by addressing sun damage.
DNA Repair Enzymes – To mitigate UV-induced damage and reduce the risk of skin cancer, topical DNA repair enzymes can be utilized. Eryfotona Actinic sunscreen contains these enzymes.
Aspirin and Melanoma – Studies suggest that daily aspirin intake may decrease the risk of melanoma in women, although this effect has not been observed in men. Further research is necessary to fully understand this relationship.
Antihistamines – While preliminary evidence suggests that daily use of the oral antihistamine desloratadine (Clarinex) may slightly lower the risk of melanoma, further research is needed for confirmation.
Expertise in Treatment
Dr. Massey is fellowship-trained in a procedure called Mohs micrographic surgery. This precise surgical technique first involves the removal of unhealthy tissue structures that rise above the skin’s surface. The next stage of the surgery continues with the removal and evaluation of microscopic layers of skin tissue lying underneath and in tissue margins around the removed growth. This meticulous process continues until examination of a removed layer confirms that no cancerous or precancerous cells remain.
Mohs surgery is highly effective in removing unhealthy cells while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible to aid in cosmetic reconstruction. As a leader in both cosmetic and cancer surgery, Dr. Massey leverages his extensive skill set to not only treat skin cancer effectively but also to restore and enhance his patients’ appearance post-surgery.
Contact Our Office
Contact us to schedule a skin cancer consultation with Dr. Massey in Santa Monica, our practice provides patients with the comfort and convenience of an on-site surgical suite and diagnostic lab. The doctor’s commitment to patient education, along with his comprehensive approach to skin cancer treatment, makes him a trusted ally in the fight against skin cancer.
